WHAT IS A NARROW DRAINAGE ANGLE?
The drainage angle is the area in the front of the eye where the fluid from inside the eye drains out of the eye. In some people, especially those who are farsighted or have cataracts, this area can become narrowed. When this happens, less fluid can leave the eye and can build up inside the eye, causing the eye pressure to increase. If the drainage angle becomes completely blocked, then a sudden rise in eye pressure can occur, which is called “angle-closure glaucoma” (ACG).
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA?
This type of glaucoma is a sudden, severe glaucoma. Symptoms of this include blurred vision, haloes, redness of the eye, pain, nausea, and vomiting. ACG can cause permanent vision loss and needs to be treated as an emergency. The treatment with laser and is called a peripheral iridotomy (PI).
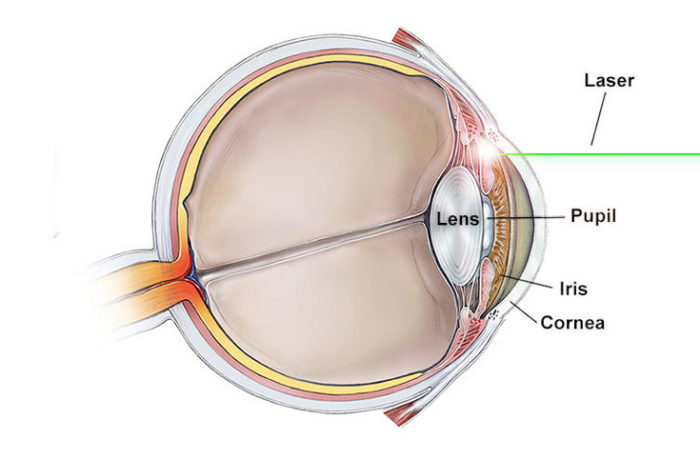
WHAT IS A PERIPHERAL IRIDOTOMY?
This is a procedure that is performed with the help of a laser to prevent or treat ACG. A contact lens is placed on the surface of the eye to help focus the laser. The laser is then used to make a microscopic opening in the iris (the coloured part of the eye) to give the fluid a different pathway to drain. A small “spark” or “thump” may be felt in the eye during the procedure, especially with the first couple shots.
WHAT ARE THE SIDE EFFECTS OF PERIPHERAL IRIDOTOMY?
PI is a very safe and well-tolerated procedure. The most common side effects include blurring, light sensitivity, mild pain around the eyes, and increased pressure in the eye. These are generally short-lived and drops are given after the procedure to minimize these effects. Occasionally, people will notice a glare for some time after the procedure, but this tends to disappear with time.